Part 3: Implementation
 The Implementation Project Lifecycle
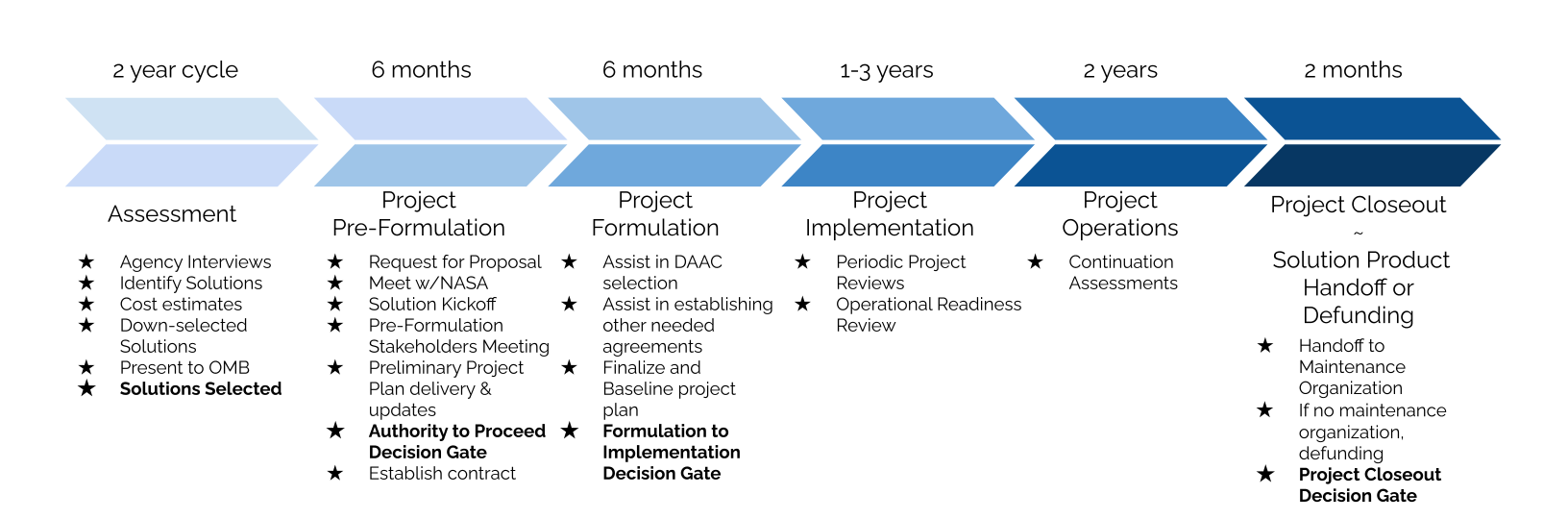
The Implementation Project Lifecycle
Overall Timeline
- Project Pre-formulation
- Project Formulation
- Project Implementation
- Project Operations
- Project Closeout
- Solution Operations Handoff or Defunding (MO action)
- Solution Closeout (MO action)
The SNWG MO Program Plan
The SNWG MO Program Plan should have been shared with you as a part of your “Welcome to the SNWG” package. The purpose of this document is to provide a framework and governance to the operations of the Management Office throughout the Program and Project lifecycles. You may also click here for a direct link to the SNWG MO Program Plan pdf
Why you care
While the SNWG MO Program Plan governs the overall process and actions of the SNWG MO, not all sections are relevant to our Projects. However, several key portions do directly impact the Projects overseen by the MO. It may not be necessary to read the entire document to understand the Office and its processes, but understanding these crucial parts is essential for the funding and ultimate success of your project.
What parts matter to you?
Key parts of the SNWG MO Program Plan for the purposes of the Project Implementation Teams are:
- 2.3.2.1 Enabling Open Science
- 5.1.2 Requirements on the SNWG Solution Projects
- 5.1.2.1 Open Source Science Requirements
- 6.2 Solution Project Implementation Collaborations
- 6.3 SNWG MO SEP Collaborations
- 12.2 Solution Project Lifecycle
Your Solution Project Plan
It is a frequent occurrence that Implementation Teams have previously provided documentation to the MO. In that case, we will often transfer that information to a Preliminary Project Plan for further completion and review by the Implementation Project Team.
| You fill out | We fill out |
|---|---|
| 1.3.1 Stakeholder Engagement Program (SEP) | 2.5 Budget and Acquisition Approach |
| 2.3 Project Schedule/ Key Project Level Milestones | 3.3 Strategy for Technology Transition |
| 2.4 Project Resources and Annual Cost Estimate | 3.4 Project Reviews |
| 3.2 Project Requirements | 4.3 Tailoring Approach |
| 3.2.1 PLR Compliance Matrix | |
| 4.1 Risk Management Strategy | |
| 4.2.1 Open Science Data Management Plan |
Decision Gates
What are they and why do we have them?
Each Decision Gate ensures that the Project has properly investigated and developed the approach, budgeting, and documentation required to move to the next phase in the Project lifecycle for maximum return of value to both the funding sources of the Project and the end user of Solution Product.
Authority to Proceed Decision Gate (ATP DG)
The Authority to Proceed Decision Gate (AtP DG) is a focused review of the initial project documentation to determine the solution project’s readiness to proceed from Pre-Formulation to Formulation and document the decision. (SNWG MO Program Plan 12.2.1.6)
The pre-formulation phase of a solution project starts after NASA learns about proposed SNWG activities in OMB’s funding request. Projects begin at this stage, but budget and scope adjustments can still be made until NASA receives and distributes funds (at the start of the fiscal year) and the project enters the formulation phase. Initiating solution projects at this stage allows pre-formulation activities to be carried out so that funds can be distributed to solution projects as soon as possible.
What you need to do before the ATP DG: Complete your preliminary Project Plan.
This includes:
- Notional OSS Objectives
How will your project adhere to Open Source Science principles during Solution Product development and operation? - Notional SEP Plan
How will your project promote stakeholder engagement throughout the Solution Product development and operation? - Outline your management approach
Team structure, partnerships, acquisition strategy, Milestone reviews
Tip: Refer to team members by their ROLE throughout the plan. Define the names associated with the role in a chart in supporting sections. - Notional schedule
Tip: Use ranges and relative times, not exact dates i.e. “2 months after project signing” “2 years after project Implementation start” Do keep in mind the limitations of final funding dates. - Resource requirements
- Project L1
- PLR Compliance matrix
- Solution Product Transition or Dissemination approach
Firm handoff plans are not required. Do include preliminary suppositions and potential handoff agencies or partners to be investigated throughout the Project lifecycle and borne to fruition by Project Closeout. - Risk Management Strategy
- Applicable Control Plans
- Required:
- Notional Open Source Data Management Plan (OSDMP)
- As needed and customized for the scope of the Project:
- CM Plan (internal note: what is CM?)
- System Security Plan
- Risk Development Plan
- Required:
- Notice to the SNWG MO of any external funding sources necessary for project success
What you need to do during:
- The Project Implementation Team presents the goals and status of their project for about 15 - 20 minutes
- The SNWG MO leads a walkthrough of the prepared Preliminary Project Plan. Your team will address any questions and make note of actions to be taken to address any concerns about the Project Plan.
What you need to do after:
- Complete any outstanding action identified as blockers to the signing of the ATP DG Memorandum.
Ultimate result: The Solution Project is authorized to proceed to the Project Formulation stage where the finer details of developing the Solution Product will be documented, the contractual agreement between NASA and the contracting Project organization is formalized.
Formulation to Implementation Decision Gate (F2I DG)
After a successful ATP DG review and the establishment of a contract between the SNWG MO and the solution project, the Formulation phase begins. This phase involves detailed planning for the implementation phase, including developing project control plans, finalizing the Project Plan, and establishing necessary agreements. Note that sometimes the formulation phase is brief, lasting just long enough to prepare for the Formulation to Implementation Decision Gate (DG).
What you need to do before:
- Finalize the Solution Project Plan (or equivalent documentation)
- Demonstrated completion of contractual agreement with the SNWG MO
- Complete any other needed project agreements as applicable:
- Inter-Agency Agreement (IAA)
- Interface Control Document(ICD) with DAAC (including finalized data Product name)
What you need to do during:
- The Project Implementation Team presents the goals and status of their project for about 15 - 20 minutes
- The SNWG MO leads a walkthrough of the prepared Project Plan. Your team will address any questions and make note of actions to be taken to address any concerns about the Project Plan.
What you need to do after:
- Complete any outstanding action identified as blockers to the signing of the F2I DG Memorandum.
Ultimate result:
The Solution Project is authorized by a Formulation to Implementation DG Decision Memorandum to move into the Project Implementation Phase, signifying that all due planning, funding, and contractual portions of the Project are within accepted parameters and do not demonstrate risk to the Solution Product development.
Operational Readiness Review (ORR)
After a successful Formulation to Implementation DG review, the project enters the Implementation phase. Here, the planned activities are carried out as described in the Project Plan, following the scheduled costs and timelines. Periodic reviews and milestone assessments are conducted as outlined in the Project Plan. The Implementation phase concludes by moving into the Operational phase upon successful completion of an Operational Readiness Review. Some Projects may not have an Operations phase and will progress directly to Closeout.
What you need to do before:
- Complete all planned data systems testing
- Resolve all test failures and anomalies
- Test, deliver, and/or install all operational supporting and enabling products necessary to support operations
- Programmatic documents are ready for review
- Stakeholder Engagement Plan deliverables
- Open Source Science Plan deliverables
- Users/operators have been trained on the correct operation of the system
- Operational contingency planning has been completed
- Operations documentation has been written, verified, and reviewed
- For Products that are being handed off to another agency: Preliminary Transition Plan is complete
- For Products that are being defunded: Preliminary Closeout Plan is complete
- Other ORR technical products prepared as necessary
- Updated cost and schedule
- Risk assessment
- Updated operations plans
- System security plan
What you need to do during:
- What do Project Teams do during an ORR?
What you need to do after:
Ultimate result
The Solution Project is authorized by an Operational Readiness Review Decision Memorandum to move into the Project Operations Phase, signifying that the Solution Project is ready to move into the Operations phase, that the Solution Product itself is Operational, and that a plan is in place to support the Solution Product through the remainder of its lifecycle.
Project Closeout Decision Gate
Upon a successful Operational Readiness Review, the project enters the Operations phase. During the operational phase, reviews called Continuation Assessments (CAs) may determine the next steps, like transferring operations, ending the project, or continuing as planned. When a project finishes its Operational phase or transfers its operations, a Project Closeout DG review is scheduled. The Project Closeout DG occurs when the solution project 1) achieves its goals and objectives, 2) reaches the end of its operational phase, 3) transfers ownership to another organization, or 4) if the solution project is terminated early.
Upon its completion, a Project is either fully defunded or fully transitioned to a maintenance agency.
What you need to do before:
- Complete final Project Summary
- Complete final project Report
- Complete Project Transition or Infusion Plan describing Product handoff to the Product receiving agency
What you need to do during:
- What do Project Teams do during an during the Project Closeout DG?
What you need to do after:
- report new technologies derived as part of the solution project to the appropriate Center Technology Transfer Office in a timely manner in accordance with NPR 7500.2 to be considered for intellectual property protection and transfer for secondary applications.
Co-design/Co-production in the Implementation Phase
What is expected of the Project team
What is expected of the Project Stakeholders
What is expected of the Product Stakeholders
Open Source Science (OSS) in the Implementation Phase
The Satellite Needs Working Group Management Office strongly encourages all SNWG Implementation team members take the time to enroll in and complete NASA’s Transform to Open Science (TOPS) OSS 101 course.